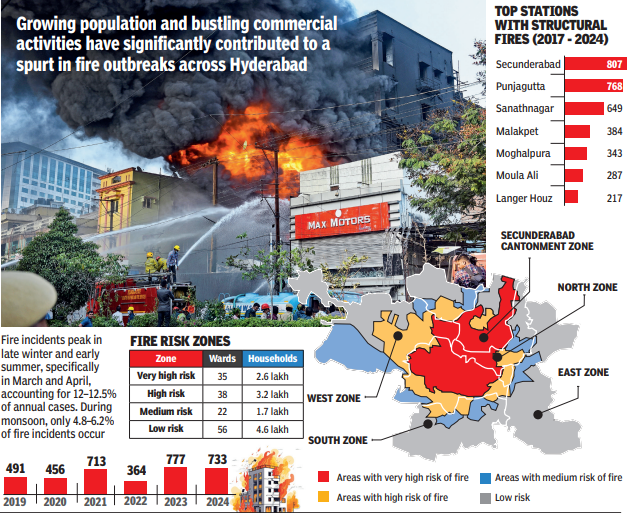
A recent study has revealed that 1.3 million residents across 260,000 households in Hyderabad are at a significantly high risk of fire accidents.
This report, titled ‘Hotspot Analysis of Structure Fires in Urban Agglomerations: A Case Study of Hyderabad,’ comes during a time of rising incidents of fire in both residential and commercial sectors. Conducted by geography professors from Osmania University and Nizam College, along with the Institute for Excellence in Higher Education in Bhopal, it was published in the Asian Journal of Geographical Research.
The research highlights that densely populated areas with a mix of commercial activities and land use are major contributors to fire hazards. The central zone of the city shows the highest percentage of high-risk fire areas at 64.86%, followed by the North East Zone at 42.56%.
35 High-Risk Wards
The study identifies 35 wards as extremely vulnerable, housing approximately 1.314 million people at a density of 17,669 individuals per square kilometer.
These wards comprise 263,197 households spread over 131 square kilometers, marking them as especially susceptible to fire risks. Key high-risk wards include Venkateshwara Colony, Gandhinagar, Red Hills, Himayatnagar, and many others.
The research utilized GIS-based hotspot analysis to pinpoint structural fires in Hyderabad, revealing over 4,000 such incidents since 2017. The primary causes of these fires include electrical failures, faulty wiring, and defective appliances, indicating a pressing need for enhanced electrical safety standards and regular inspections.
Careless Smoking as a Major Cause
Furthermore, the study attributes fire incidents largely to the area’s urban density, commercial activities, and infrastructure vulnerabilities, with careless smoking cited as a leading cause, along with mechanical heat or sparks. Seasonal climatic variations and rising electricity demand also escalate fire risks.
“Hyderabad’s growing industrial zones and densely populated residential areas pose significant challenges in managing fire risks. The lack of adequate fire safety infrastructure, coupled with congested urban centers and changing industrial patterns, calls for comprehensive spatial analyses of fire-prone areas to enhance fire response strategies. The study emphasizes the need for strategic interventions, such as relocating or establishing fire stations in high-risk zones, improving electrical safety regulations, launching targeted public awareness campaigns, and adopting climate-responsive urban planning,” the study remarks.
Importance of Fire Station Placement
The study indicates regions such as Gachibowli, Chandanagar, Secunderabad Cantonment, and Tirumalagiri are found in extended response zones. To ensure prompt responses, the report suggests either constructing new fire stations or upgrading existing infrastructure in these regions.
Additionally, high coverage areas in the delayed response zone are immensely important because of their commercial and residential importance. The study underscores that strategically locating fire stations is vital.
“Research on fire incidents in Hyderabad from 2017 to 2024 was conducted across various Greater Hyderabad zones, aiming to identify fire-prone regions and their underlying causes. Data collection and analysis spanned eight months before the findings were finalized,” stated R Veena, professor in the Department of Geography at Osmania University.